Mapping your programme level assessment and feedback
This guide provides you with ideas to help a team discuss assessment and feedback design. This guide should be read and used in conjunction with the other guides on this site.
Sharing module assessment and feedback practices
Have each module leader present a brief overview of their module's assessment methods and feedback practices, including:
- Types of assessments used (for example, essays, presentations, group projects, exams)
- Frequency and timing of assessments
- Feedback mechanisms (for example, written comments, rubrics, one-on-one meetings)
- How assessment and feedback align with module learning outcomes
Create a way of representing each of this assignment to allow the team to see the assessment structure across the programme. For instance, post it notes across a table.
Figure 1 below, an example showing an arrangement of boxes in the form of a grid to represent different modules, and the use of arrows to link assessments across the programme.

Encourage team members to ask questions and discuss the strengths and challenges of each module's approach.
Identifying assessment and feedback pathways
As a team, identify common themes and skills that are developed across the programme, such as:
- Research and critical thinking skills
- Writing and communication skills
- Group work and collaboration
- Presentation skills
- Problem-solving and analysis
Discuss how assessments in each module contribute to the development of these skills and how feedback can be used to support student progress.
Create a visual map or flowchart that illustrates the connections between assessments and skill development across the programme (Figure 1).
Enhancing coherence and progression
Identify opportunities for scaffolding and progression of skills throughout the programme. Consider:
- How assessments can build upon each other to support student growth
- How feedback from one assessment can inform student performance in subsequent assessments
- How to ensure a balance of assessment types across the programme
- How to clearly and consistently communicate to students about the linkages between assessments
Discuss strategies for providing consistent and effective feedback, such as:
- Developing programme-wide feedback guidelines as discussed in the Feedback section
- Encouraging student self-reflection and goal-setting based on feedback
- Providing opportunities for students to apply feedback in future assessments
- Discussing strategies for supporting neurodivergent students by using some of the ideas in Inclusive Assessment section
Action planning and implementation
Based on the discussions, develop an action plan for enhancing the programme's assessment and feedback strategy. This may include:
- Revising assessment methods or timing in specific modules
- Developing new feedback tools or resources
- Creating opportunities for cross-module collaboration and skill development
- Establishing a timeline for implementing changes and reviewing progress
- Creating materials for students at each level so they can understand the linkages across the programme and how particular skills and knowledge will be developed through programme assessment and feedback.
Assign responsibilities and set regular check-in meetings to ensure progress and address any challenges that arise.
Calibrating assessment marking standards
Schedule one or two annual meetings dedicated to calibrating assessment marking standards across the programme team.
Example of assessment and feedback mapping document
There are many different ways to visualise your programme that will highlight different aspects to you and the team. Here are two examples.
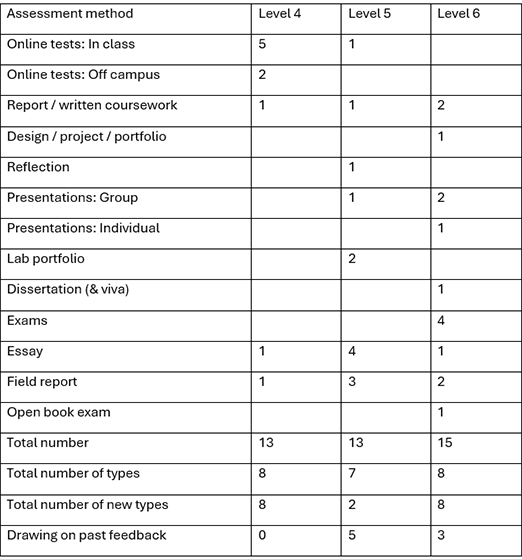
Assessment methods table
The Assessment methods table summarises the types and frequencies of assessments used across three educational levels: Level 4, Level 5, and Level 6. It lists 11 assessment methods, such as online tests, reports, presentations, and exams. The table shows the number of times each method is used per level, totals for the number of assessments, unique types, and new types introduced at each level. It also indicates how many assessments build on past feedback. This table helps identify gaps and inconsistencies in assessment practices, enabling educators to evaluate and optimize their assessment strategies.
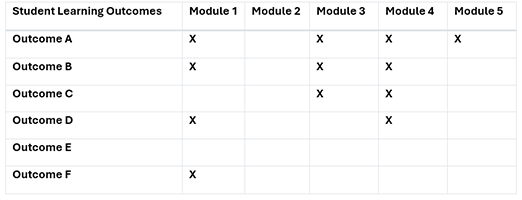
Learning outcomes table
The Learning outcomes table maps student learning outcomes to specific modules. It lists six outcomes (A-F) and five modules (1-5). An "X" indicates an outcome is covered in a module. The table shows which outcomes are emphasized in each module and reveals patterns of progression and reinforcement. Outcome A is consistently covered, while Outcome E is absent. Outcomes B, C, and D are introduced early and revisited later. This visualization helps ensure all desired outcomes are addressed, identifies gaps, and informs curriculum design decisions to enhance the learning experience.